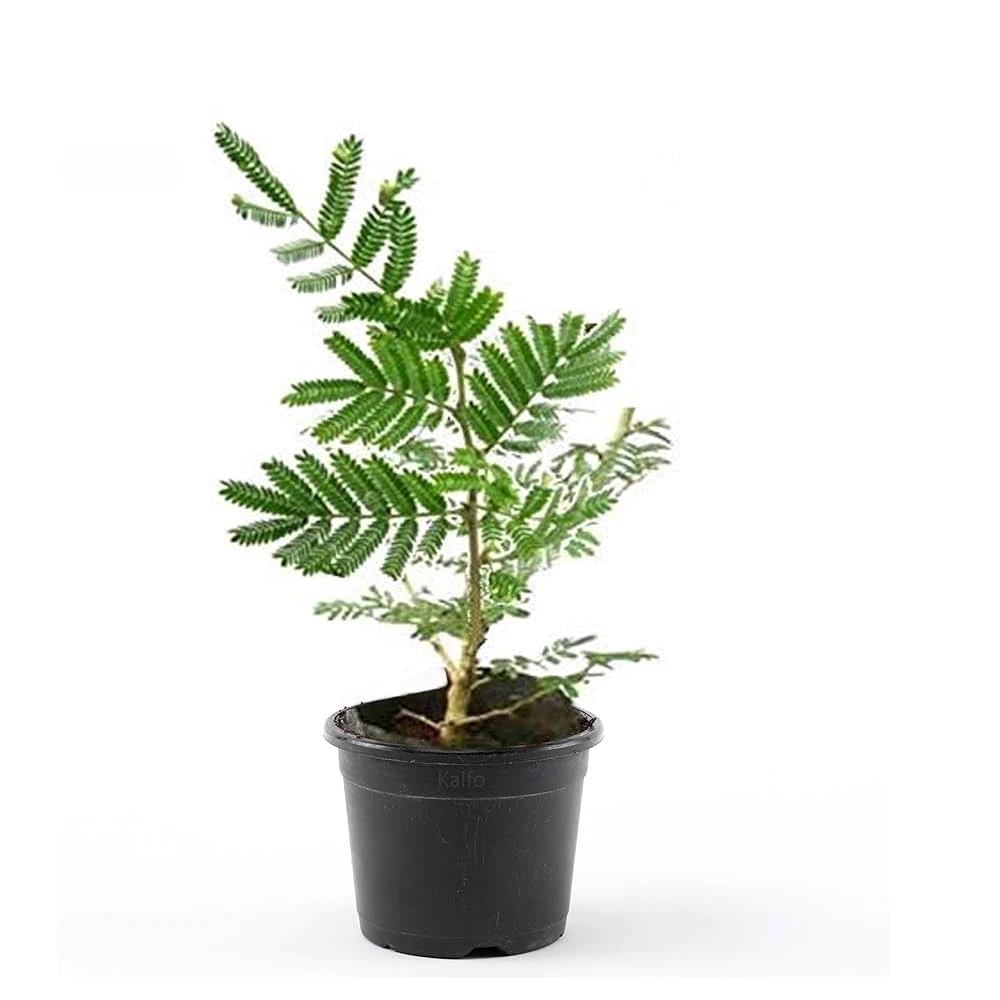
The Shami plant, scientifically known as Prosopis cineraria, is a medium-sized, evergreen tree native to arid and semi-arid regions of South Asia. It's also known as Khejri or Indian mesquite. The Shami is renowned for its drought resistance, cultural significance in Hinduism, and various practical uses.
Physical Characteristics:
Size: Typically grows to 10 meters tall, with a spreading canopy.
Bark: Grayish-brown and rough, often with thorns on the branches.
Leaves: Small, compound, and feathery, arranged alternately on the stem.
Flowers: Small, yellow-green, and fragrant, appearing in dense clusters.
Fruit: Long, brown pods containing seeds.
Ecological and Cultural Significance:
Drought Resistance: Thrives in dry, sandy soils and extreme heat.
Hinduism: Revered in Hinduism, particularly associated with Lord Shiva and worshipped during festivals like Dussehra.
Cultural Uses: Leaves and flowers are used for worship, and the tree holds cultural significance in various regions.
Medicinal Uses: Bark, leaves, and fruits have traditional medicinal uses.
Other Uses: Used for fuelwood, timber, fodder, and soil conservation.